Release date 2024.9.2
Characteristics & Mechanism of Action
Zuranolone is a novel antidepressant that exerts its effects by acting on GABAA receptors and enhancing GABA signaling, offering a new mechanism of action for depression treatment1) (Figure 1).
(Fig 1)Mechanism of Action of Zuranolone
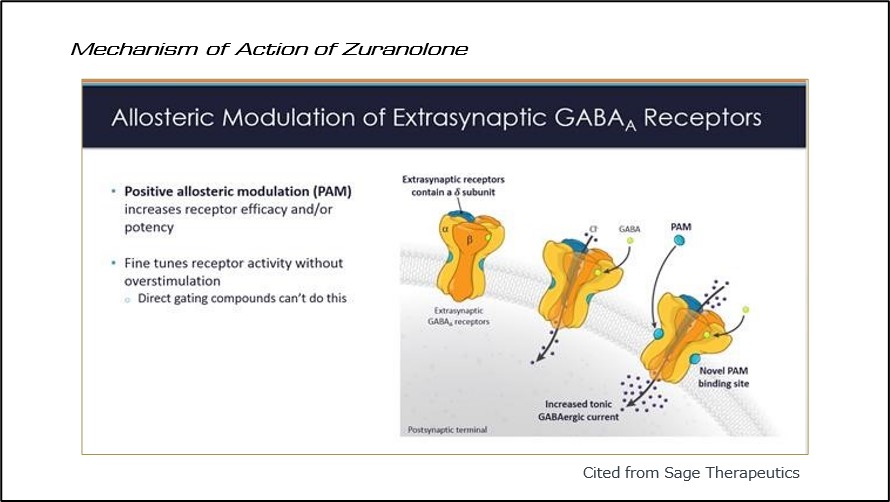
Due to its mechanism of action, it is referred to as a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator.
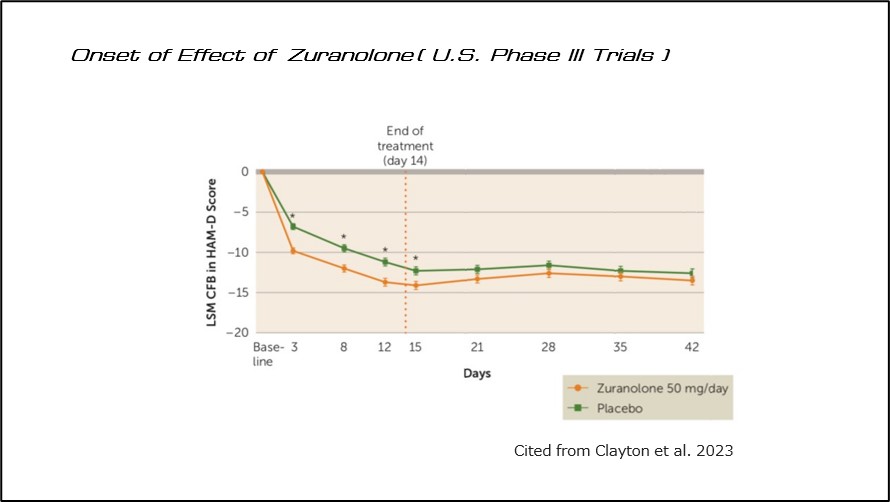
It has the advantage of rapid onset, with effects observable from the third day of administration, and excellent tolerability2) (Figure 2).
(Fig 2)Onset of Effect of Zuranolone(U.S. Phase Ⅲ Trials)
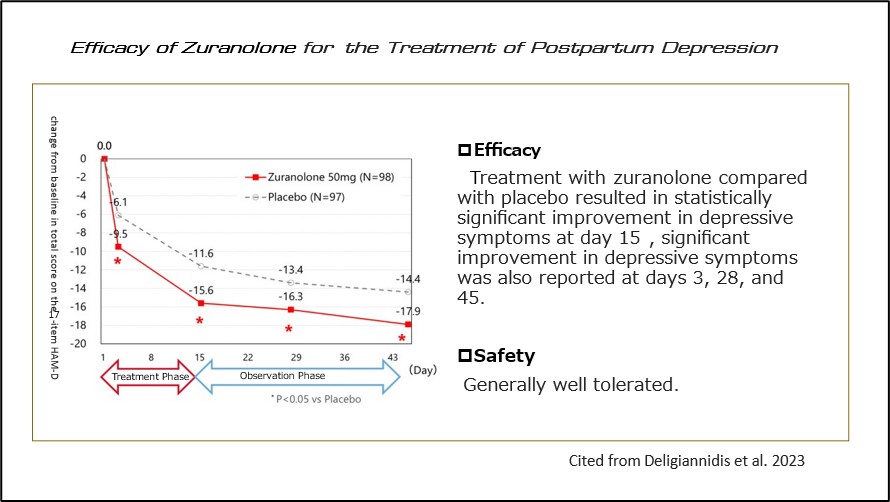
Its efficacy in treating postpartum depression has also been demonstrated3) (Figure 3).
On August 4, 2023, the U.S. FDA approved Zuranolone (brand name: Zurzuvae) as the first oral antidepressant for postpartum depression.
(Fig 3)Efficacy of Zuranolone for the Treatment of Postpartum Depression
Development History
Zuranolone was developed from the endogenous neurosteroid allopregnanolone (Figure 4).
(Fig 4)Chemical Structures of Allopregnanolone and Zuranolone
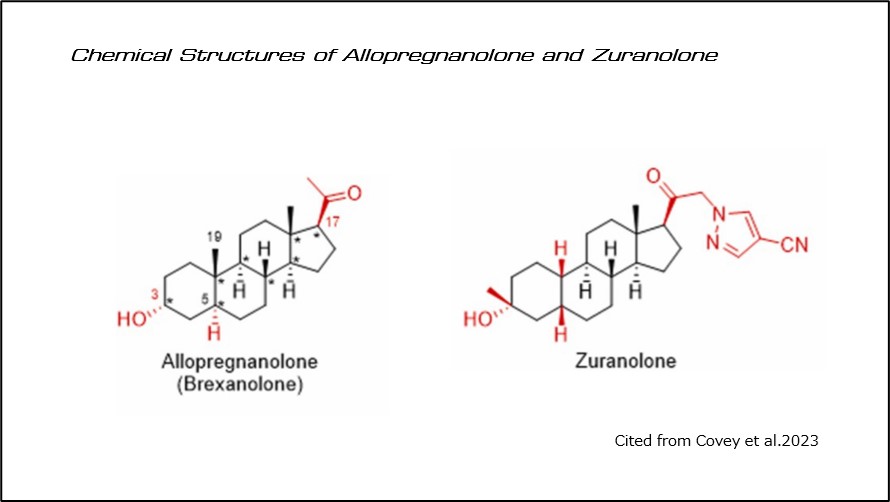
Allopregnanolone itself had already been approved in the U.S. in 2019 as a treatment for postpartum depression under the brand name Zulresso (brexanolone) as an intravenous drug.
Currently, it has been shown to be effective for both postpartum depression and major depressive disorder4),5).
Dosage & Administration
In the U.S., for postpartum depression, Zuranolone is administered once daily in the evening with a fat-containing meal at a dose of 50 mg for 14 days.
It has the unique feature of not requiring dose or duration adjustments like traditional antidepressants.
Pharmacokinetics
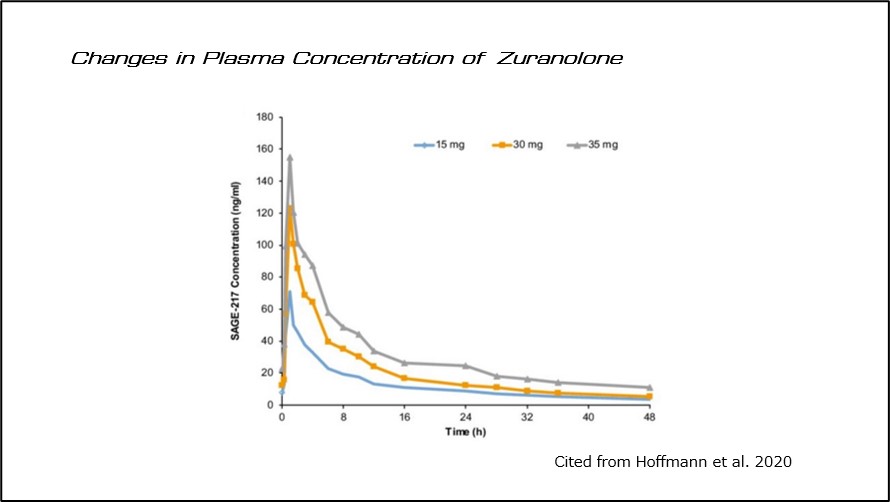
After oral administration of Zuranolone 30 mg, the blood concentration reaches its peak after approximately 1 hours and halves after about 14 hours6), (Figure 5).
(Fig 5)Changes in Plasma Concentration of Zuranolone
Side Effects
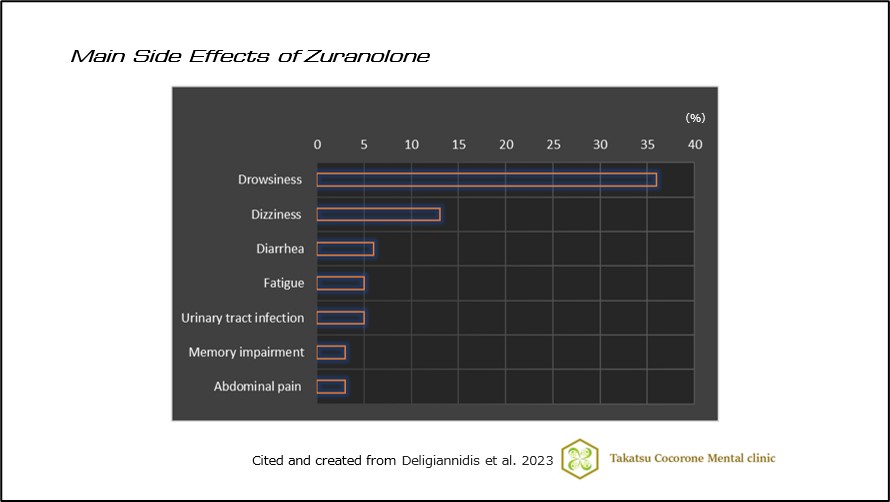
The main reported side effects are as follows3) (Figure 6):
- Drowsiness(36%)
- Dizziness(13%)
- Diarrhea(6%)
- Fatigue(5%)
- Urinary tract infection(5%)
- Memory impairment(3%)
- Abdominal pain(3%)
(Fig 6)Main Side Effects of Zuranolone
References
- 1) Cutler AJ, et al. : Understanding the mechanism of action and clinical effects of neuroactive steroids and GABAergic compounds in major depressive disorder. Transl Psychiatry, 13 : 228, 2023.
- 2) Clayton AH, et al. : Zuranolone for the Treatment of Adults With Major Depressive Disorder: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Am J Psychiatry, 180 : 676-684, 2023.
- 3) Deligiannidis KM, et al. : Zuranolone for the Treatment of Postpartum Depression. Am J Psychiatry, 180 : 668-675, 2023.
- 4) Raja A, et al.: Evaluating the safety and efficacy of zuranolone in the management of major depressive disorder and postpartum depression, with or without concurrent insomnia: a rigorous systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psychiatry, 15: 1425295, 2024.
- 5) Fayoud AM, et al.: The efficacy and safety of Zuranolone for treatment of depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 241: 1299-1317, 2024.
- 6) Hoffmann E, et al.: SAGE-217, A Novel GABAA Receptor Positive Allosteric Modulator: Clinical Pharmacology and Tolerability in Randomized Phase I Dose-Finding Studies. Clin Pharmacokinet, 59: 111-120, 2020.
Column list
- Characteristics, Mechanism of Action, and Side Effects of Zuranolone
- Characteristics, Mechanism of Action, and Side Effects of Auvelity
- Characteristics, Mechanism of Action, and Side Effects of Esketamine
- Latest Comparison of Weight Changes Due to Antidepressants
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics in Acute Schizophrenia: Latest Report
- Comparison of Efficacy and Tolerability of Drug Treatments in Acute Manic Episodes of Bipolar Disorder: Latest Report
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Drug Treatment in Maintenance Therapy for Psychotic Depression

- 頭が働かない
- 寝つきが悪い
- やる気が起きない
- 不安で落ち着かない
- 朝寝坊が多い
- 人の視線が気になる
- 職場に行くと体調が悪くなる
- 電車やバスに乗ると息苦しくなる

- うつ病
- 強迫性障害
- 頭痛
- 睡眠障害
- 社会不安障害
- PMDD(月経前不快気分障害)
- パニック障害
- 適応障害
- 過敏性腸症候群
- 心身症
- 心的外傷後ストレス障害
- 身体表現性障害
- 発達障害
- ADHD(注意欠如・多動症)
- 気象病・天気痛
- テクノストレス
- バーンアウト症候群
- ペットロス(症候群)
- 更年期障害
- 自律神経失調症