Release date 2024.9.18
In August 2024, Huang et al. reported the latest comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of drug treatments for acute manic episodes of bipolar disorder 1).
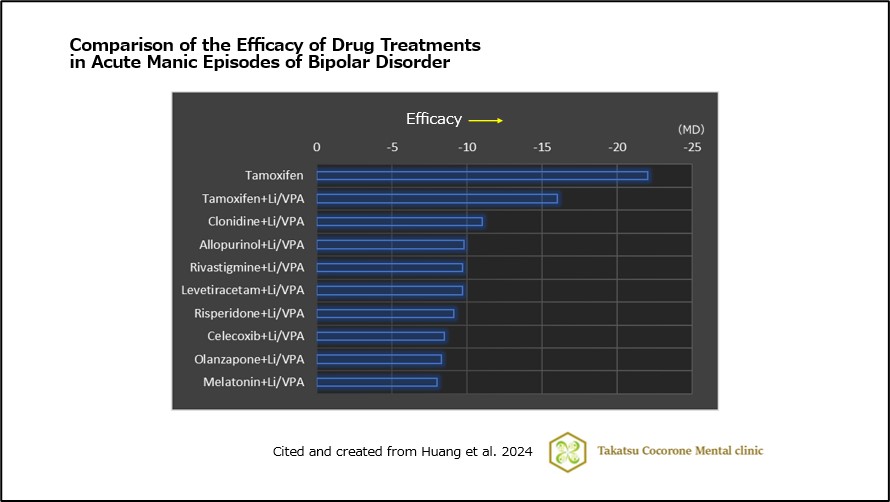
The following drugs were reported as the top 10 in terms of efficacy (Figure 1):
- Tamoxifen
- Tamoxifen + Li/VPA
- Clonidine + Li/VPA
- Allopurinol + Li/VPA
- Rivastigmine + Li/VPA
- Levetiracetam + Li/VPA
- Risperidone + Li/VPA
- Celecoxib + Li/VPA
- Olanzapine + Li/VPA
- Melatonin + Li/VPA
(Fig 1)Comparison of the Efficacy of Drug Treatments in Acute Manic Episodes of Bipolar Disorder
The following drugs showed favorable tolerability results (Figure 2):
- Olanzapine
- Paliperidone
- Quetiapine
- Ziprasidone
- Risperidone
- Divalproex
- Haloperidol
(Fig 2)Comparison of the Tolerability of Drug Treatments in Acute Manic Episodes of Bipolar Disorder

Antimanic Effect of Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen is a treatment for breast cancer that inhibits the binding of estrogen to estrogen receptors, thereby suppressing cancer growth.
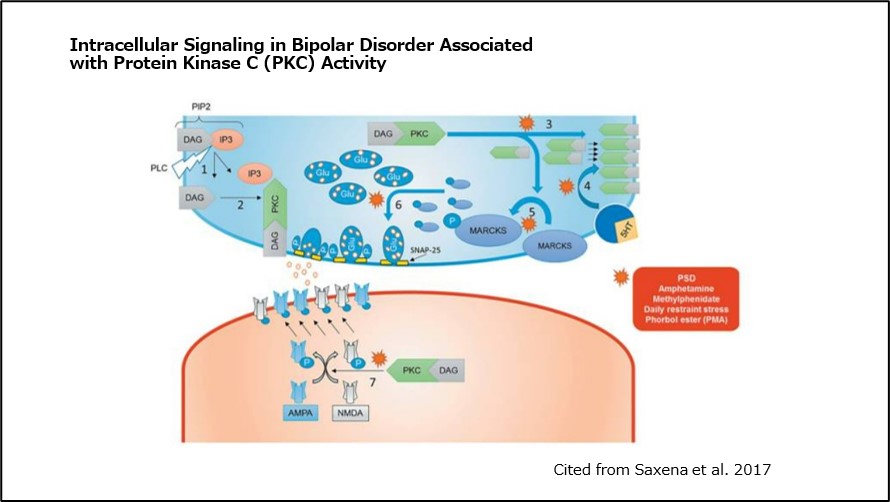
Tamoxifen is thought to exert its antimanic effect by inhibiting the activity of protein kinase C (PKC) 2).
Activation of PKC has been reported to promote various intracellular signaling pathways involved in mania 3).
(Fig 3)Intracellular Signaling in Bipolar Disorder Associated with Protein Kinase C (PKC) Activity
Antimanic Effect of Clonidine
Clonidine, which is used in the U.S. as a treatment for ADHD, was approved by the FDA in May 2024 as the first liquid formulation for ADHD treatment (Onyda XR).
Similar to its effect on ADHD, its ability to reduce noradrenergic transmission is thought to be involved in its antimanic effect 4).
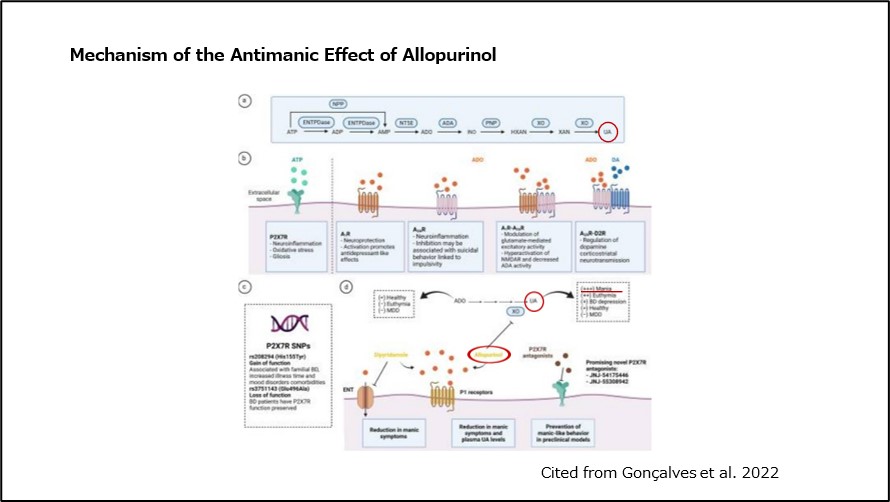
Antimanic Effect of Allopurinol
ATP, which is involved in cellular energy production, is metabolized into uric acid. Elevated uric acid levels have been reported to be associated with mania and impulsivity.
Allopurinol exerts its antimanic effect by suppressing the increase in uric acid levels 5).
Additionally, allopurinol is also considered an adenosine modulator because it regulates the metabolism of adenosine, which is related to its antimanic effect 6).
(Fig 4)Mechanism of the Antimanic Effect of Allopurinol
Antimanic Effect of Rivastigmine
The noradrenergic-cholinergic system in the central nervous system has long been reported to be involved in mood regulation 7).
Specifically, in bipolar disorder, inhibition of acetylcholine transmission leads to mania, while enhancement of acetylcholine transmission stabilizes mood 8).
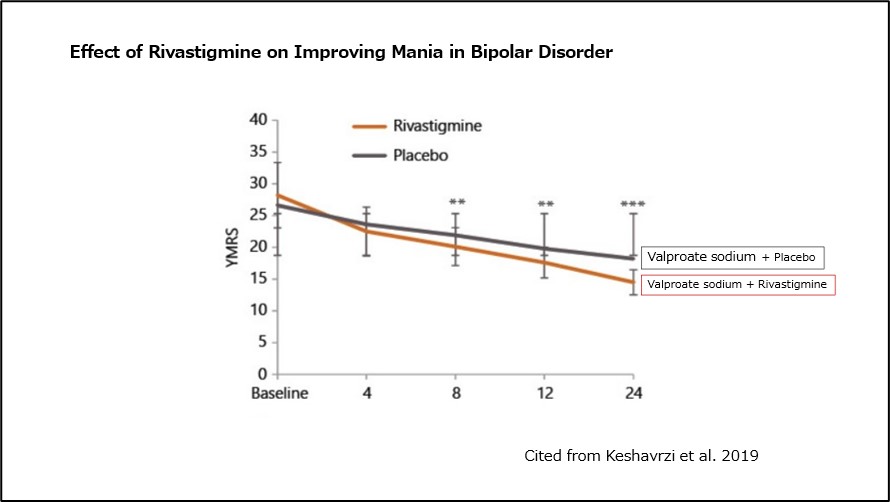
Keshavrzi et al. conducted a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with acute manic episodes of bipolar disorder, dividing them into a group receiving valproate sodium + placebo and a group receiving valproate sodium + rivastigmine 9).
The results showed a significant improvement in mania from week 8 in the valproate sodium + rivastigmine group compared to the valproate sodium + placebo group.
(Fig 5)Effect of Rivastigmine on Improving Mania in Bipolar Disorder
Antimanic Effect of Levetiracetam
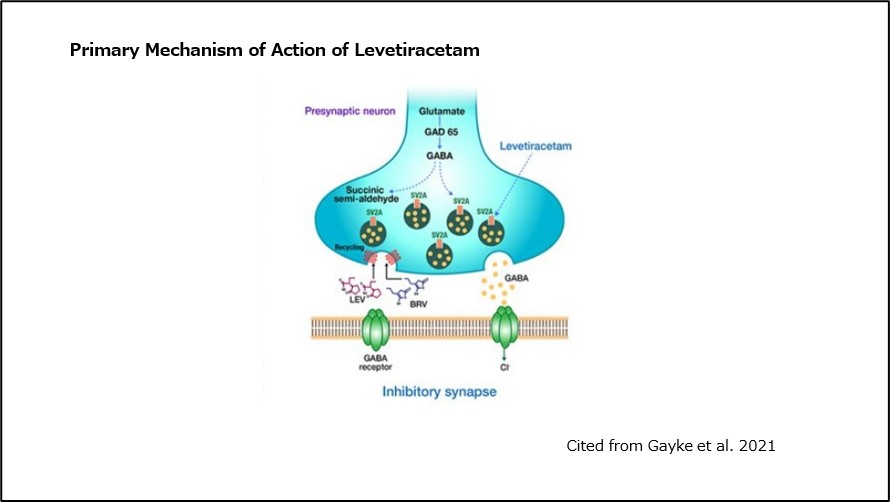
It has been reported that the concentration of GABA in the prefrontal cortex of the brain is elevated in patients with bipolar disorder 10).
These findings suggest a functional abnormality in the GABAergic system in patients with bipolar disorder.
Levetiracetam binds to synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A) in the brain and modulates the release of GABA from synapses.
The regulation and enhancement of the GABAergic system by levetiracetam are thought to be involved in its antimanic effect 11) .
(Fig 6)Primary Mechanism of Action of Levetiracetam
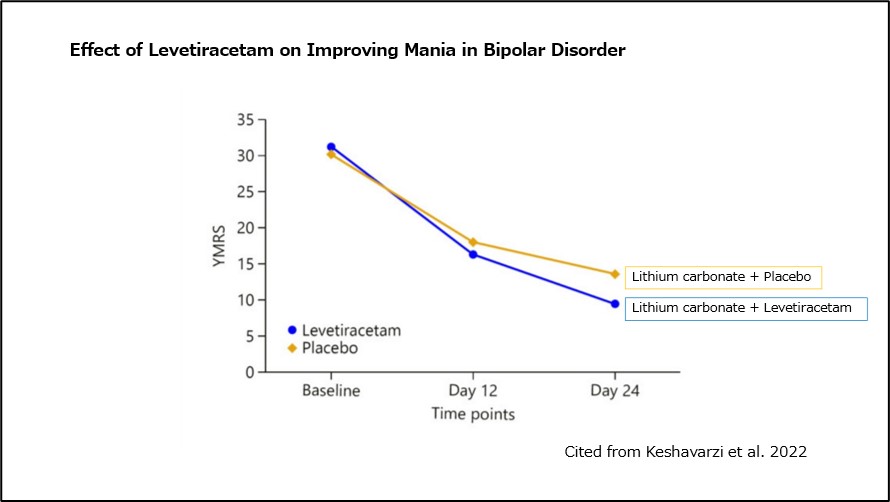
Keshavarzi et al. conducted a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 2022 with patients with acute manic episodes of bipolar disorder being treated with lithium carbonate.
The patients were divided into a group receiving lithium carbonate + placebo and a group receiving lithium carbonate + levetiracetam 12).
The results showed a significant improvement in mania in the lithium carbonate + levetiracetam group compared to the lithium carbonate + placebo group.
(Fig 7)Effect of Levetiracetam on Improving Mania in Bipolar Disorder
Conclusion
The findings of this report are not immediately applicable to clinical practice. In reality, treatments guided by current guidelines, such as lithium carbonate or valproate sodium as the main agents combined with antipsychotic drugs, will continue to be used.
However, in cases where existing treatments are difficult due to side effects or poor tolerability, or in treatment-resistant cases, the results of this study may be applied promptly.
It is known that patients with bipolar disorder tend to have high uric acid levels 13).
For patients with bipolar disorder with elevated uric acid levels, febuxostat is preferred in cases of allergic diseases due to the risk of rash, but otherwise, treatment with allopurinol is recommended.
The treatment of manic episodes in bipolar disorder requires not only the prevention of subsequent depressive episodes and consideration of physical comorbidities but also the long-term protection of cognitive function.
In this regard, treatments such as rivastigmine, a nootropic drug, and levetiracetam, which was also developed as a nootropic, are expected to produce favorable outcomes for cognitive function when combined with lithium carbonate, which has been shown to prevent cognitive decline 14).
While these treatments have been reported as new adjunct therapies in recent years, they are expected to lead to better treatment outcomes when added to conventional therapies.
References
- 1) Huang W, et al.: Comparative efficacy, safety, and tolerability of pharmacotherapies for acute mania in adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Mol Psychiatry, 2024.
- 2) Bagdadi N, et al.: The Use of Tamoxifen as a Potential Treatment for Bipolar Disorder. Psychiatry Clin Psychopharmacol, 31: 344-352, 2021.
- 3) Saxena A, et al.: Role of Protein Kinase C in Bipolar Disorder: A Review of the Current Literature. Mol Neuropsychiatry, 3: 108-124, 2017.
- 4) Singal P, et al.: Efficacy and Safety of Clonidine in the Treatment of Acute Mania in Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci, 13: 547,2023.
- 5) Gonçalves MCB, et al.: The Purinergic System as a Target for the Development of Treatments for Bipolar Disorder. CNS Drugs, 36: 787-801, 2022.
- 6) Hirota T, Kishi T.: Adenosine hypothesis in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial of adjuvant purinergic modulators. Schizophr Res, 149: 88-95, 2013.
- 7) Dulawa SC, Janowsky DS.: Cholinergic regulation of mood: from basic and clinical studies to emerging therapeutics. Mol Psychiatry, 24: 694-709. 2019.
- 8) van Enkhuizen J, et al.: The catecholaminergic-cholinergic balance hypothesis of bipolar disorder revisited. Eur J Pharmacol, 753:114-26, 2015.
- 9) Keshavrzi A, et al.: Effect of Rivastigmine (Acetyl Cholinesterase Inhibitor) versus Placebo on Manic Episodes in Patients with Bipolar Disorders: Results from a Double Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Neuropsychobiology, 78: 200-208, 2019.
- 10) Simmonite M, et al.: Medial Frontal Cortex GABA Concentrations in Psychosis Spectrum and Mood Disorders: A Meta-analysis of Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Studies. Biol Psychiatry, 93: 125-136, 2023.
- 11) Muralidharan A, Bhagwagar Z.: Potential of levetiracetam in mood disorders: a preliminary review. CNS Drugs, 20: 969-79, 2006.
- 12) Keshavarzi A, et al.: Levetiracetam as an Adjunctive Treatment for Mania: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Neuropsychobiology, 81: 192-203, 2022.
- 13) Chatterjee SS, et al.: Serum uric acid levels in first episode mania, effect on clinical presentation and treatment response: Data from a case control study. Asian J Psychiatr, 35:15-17, 2018.
- 14) Lu Q, et al.: Lithium Therapy's Potential to Lower Dementia Risk and the Prevalence of Alzheimer's Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Eur Neurol, 87: 93-104, 2024.
Column list
- Characteristics, Mechanism of Action, and Side Effects of Zuranolone
- Characteristics, Mechanism of Action, and Side Effects of Auvelity
- Characteristics, Mechanism of Action, and Side Effects of Esketamine
- Latest Comparison of Weight Changes Due to Antidepressants
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics in Acute Schizophrenia: Latest Report
- Comparison of Efficacy and Tolerability of Drug Treatments in Acute Manic Episodes of Bipolar Disorder: Latest Report
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Drug Treatment in Maintenance Therapy for Psychotic Depression

- 頭が働かない
- 寝つきが悪い
- やる気が起きない
- 不安で落ち着かない
- 朝寝坊が多い
- 人の視線が気になる
- 職場に行くと体調が悪くなる
- 電車やバスに乗ると息苦しくなる

- うつ病
- 強迫性障害
- 頭痛
- 睡眠障害
- 社会不安障害
- PMDD(月経前不快気分障害)
- パニック障害
- 適応障害
- 過敏性腸症候群
- 心身症
- 心的外傷後ストレス障害
- 身体表現性障害
- 発達障害
- ADHD(注意欠如・多動症)
- 気象病・天気痛
- テクノストレス
- バーンアウト症候群
- ペットロス(症候群)
- 更年期障害
- 自律神経失調症